Design Case study
Truck for era 2020
Advance Concept Truck Design
by
Overview of Cv’s:
The Indian Auto Industry is buzzing with growth and activity. With a population of over one billion and an economic growth at over 7%, India is the new business hub. The Automotive sector is one of the core industries of the Indian economy whose prospects is reflective of the economic resilience of the country. With 4% contribution to the GDP, and nearly 5% of the total industrial output, the automotive sector has become a significant contributor to the exchequer. Continuous economic liberalization over the years by the government of India has resulted in making India as one of the prime business destination for many global automotive players.
Indian Automobile Industry Today:
Second largest 2 wheelers manufacturers in the world.
• World largest Motorcycle manufacturer is in India.
• Second Largest tractor manufacturer in the world.
• Fifth largest commercial vehicle manufacturer in the world.
• Fourth largest Car market in Asia.
Commercial Vehicle Industry: Scenario:
Commercial vehicles sales have grown at a 4.4% CAGR over the last decade and the segment has also demonstrated cyclical trends. The commercial vehicles segment grew by 36.12 per cent during the April- February 2007 period, while three wheeler sales grew by 14.5 per cent. For the same period, two wheeler sales grew by 12.56 percent, with motorcycles segment witnessing a growth of 14.45 per cent. Growth in the commercial vehicle sector is dependent on the general economic trend, development of infrastructure projects, Transport economics and availability of freight, replacement period of vehicles, easy availability of credit and conducive government policies.
Types of Commercial Vehicles:
The commercial vehicle sector can be broadly categorized as Light Commercial Vehicles (LCV) and Medium & Heavy Commercial vehicles (M&HCV) based on the Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) of the vehicle.
The HCV segment can be further classified into three segments based on gross vehicle weight as follows:
• ICV: Intermediate commercial vehicle with GVW of 8 to 10 ton.
M&HCVs are used for transport of heavy commodities such as steel cement, fertilizers etc. LCVs are preferred for high volume low bulk cargo such as consumer goods, textiles, for short distance haulage. On the basis of fuel used, vehicles can be further classified as diesel or petrol driven vehicles. Diesel vehicles are economical and more popular in India. Petrol vehicles have strong niche in hilly/ cold areas where vehicles require a cold start.
Emerging Trends in Cv’s:
• Increased investment in road infrastructure.
• Cheaper finance.
• Multi-axle vehicles.
• A shift to tractor trailer combinations.
• Higher power-to-weight ratio vehicles.
• The Indian market is for low priced rugged vehicles.
• Introduction of technologically superior vehicles.
• Use of hybrid technologies.
• Better freight management.
• Use of GPS, GPRS for better communication.
• Digital Displays.
• Better Ergonomics.
• Better safety Cab Designs.
Conclusion:
Transport technology is in an exciting phase of development. One of the main catalysts bringing about consolidation in the industry will be the emergence of heavy duty, four-lane highways (Golden Quadrilateral).
Thanks to satellite communication, almost all trucks will be equipped with tracking facilities as Global Positioning Systems. Two-way communication between truck operators and trucks will also become available at a more economically viable rate. The economic development has brought to the fore the modern problems of urbanization pollution, bad vehicular emissions and increase in road accidents In this scenario, certain incentives or concessions need to be provided to retire/ replace old vehicles and modernize fleet.
Model of Surface Transport:
Point - to - Point System: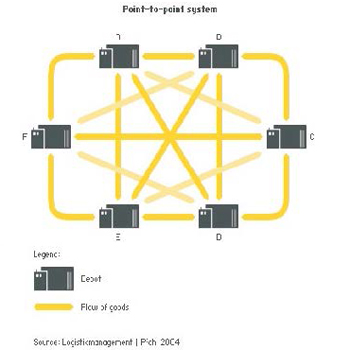

Hub - and - Spoke System: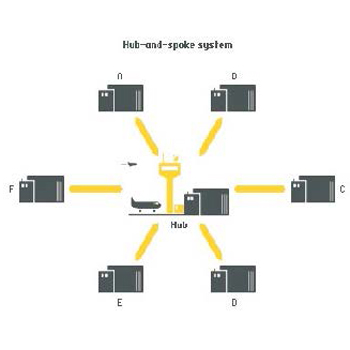

Collage of Indian Trucks:

Study of Concept trucks:
Concept cars and trucks are a cross between a designer's imagination and the real world. Concept trucks don't arrive in dealer showrooms as-is, but they give us a good preview of truck design trends.
The aim of such projects is to highlight the company profile and growth. Concept trucks are a cross between a designer's imagination and the "real world" vehicles available to consumers. In recent years some concepts have looked a whole lot like the vehicles eventually available for sale, but most concepts have far-out features that don't make it to production if manufacturers decide to produce a vehicle.
The Concept trucks reflect the near and future technologies and imagination. In the world of trucks, trends such as to hide the A pillar, needs a advance technoloy. This in terms of Day light opening and overall vehicle form looks more integrated.
The concept trucks are also made keeping in mind the feasibility of the concept to be in future production. Commercial vehicle segment has been neglected largely in India considering styling, safety and technoloy.
The Renault Radiance:
In terms of exterior design, while Radiance shares some obvious design cues with its more mainstream siblings, the first thing which strikes you about it is its sleek, aerodynamic and modern shape which defies traditional, box-style truck design.
Moving from the front to the rear of the new ‘dream truck’, the visionary front end includes large air inlets to give extra engine cooling and foldaway steps which still allow easy cabin access but don’t interfere with the truck’s curvaceous lines. In keeping with Radiance’s futuristic lines, two exterior cameras are mounted on the cab’s aerofoil which eliminate all blind spots and give superior visibility, while the modern front headlights which have a hint of Espace about them, are multi- directional so that they can be adapted to specific driving conditions, including city, fog and motor way mode.
To maintain the truck’s streamlined design, at the rear of the cab, Renault has created an ingenious aluminum connecting unit for the electrical and tyre cables which fit to the trailer, which with its retractable cables, works in a similar way to a modern vacuum cleaner’s power cable so that no ugly cables can detract from the vehicle’s modern looks.
Volvo concept 2020:
Out of the darkness we see it. Illuminated by high intensity headlights and a strangely familiar neon-lit grille motif. Beneath the towering yet slender cab the engine hums like a German washing machine, quiet, purposeful.
Seated in the figure hugging pre-programmed memory seat you reach out to the touch sensitive dashboard and select the instruments you want displayed during your journey but to where and with what?
Soon we’ve made our way to one of the many designated Trans-European 'Green Freight Corridors' where you're soon joined by other Vision 2020 trucks...and naturally using your integrated guidance system and adaptive cruise control with automated distance sensing it's not long before you're running in a convoy of Vision 2020 road trains.
Understanding Cab Design Elements & Modularity Concept:
























