Jean Piaget has been one of the most popular and influential experts in the field of developmental psychology and education. He stated that learning occurs in children through the process of adaptation, an active process where children construct knowledge structures through experience and interaction with their environment. Adaptation could be further divided into two processes – assimilation (fitting new information into pre-existing cognitive schemas or knowledge) and accommodation (altering pre-existing schemas in order to fit in the new information). This discourse of actively creating knowledge by building upon previous experiences through interaction with environment is known as constructivism, which is very popular among a lot of other researchers and actively used in the field of interaction design. Seymour Papert expanded this discourse into constructionism stating that Piaget’s active learning process works best when children are consciously engaged in constructing public entities. This has been widely adopted in the design of toys, games, and learning technologies that allow the child to author the experiences, rather than passively following a script.
Piaget further identifies four major factors that affect the development process. The design implications of these factors are briefly discussed below:
• Maturation: Artefacts & technology need to adapt to the limited physical and cognitive capabilities of children at a specific age.
• Experience: Enabling environment such that children can naturally learn by experiencing different artefacts to form their knowledge (schemas).
• Social Interaction: Enabling social interactions through technology such that knowledge in the form of information and strategies can be passed from one generation to the next.
• Emotions and Motivation: Learning and developmental activities need to be made relevant to children’s lives and interests.
Apart from the above theory, one of the most significant contributions from Piaget’s theory is the identification of developmental stages. He stated that all children go through a series of stages in their intellectual development, each related to certain typical behaviours and abilities. These stages are:
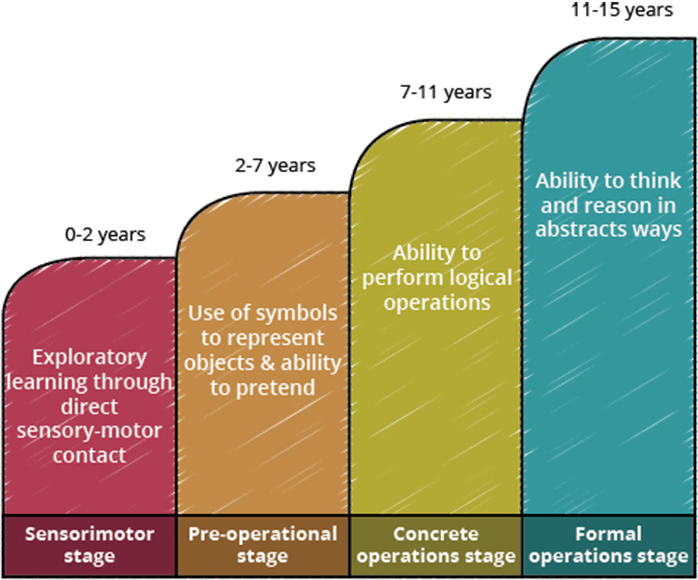
Design Recommendations Based on Piaget’s Theory:
1) Children at pre-operational stage cannot concentrate on more than one characteristic of an object at a time, thus they have trouble in interacting with hierarchical elements in an interface. Providing alternative options together instead of a hierarchy is a better option in the design of interfaces. Hierarchies are useful for children from the concrete operations stage.
2) Learning applications which involve abstract concepts like deductive reasoning and logically analysing options are understood for children only in the formal operations stage, and are not ideal for younger children.
3) Children at pre-operational stage are ego-centric and can’t be partnered in participatory design processes and methods. This could be better achieved in children from concrete operations stage and later.

